“Discover How Smartphone GPS Works technology revolutionizes navigation with pinpoint accuracy, enhanced connectivity, and real-time tracking for a seamless mobile experience.”
Introduction: Understanding How Smartphone GPS Works
Smartphone GPS technology has redefined the traditional way navigations are made.
Millions are enjoying real-time location tracking and precise positioning thanks to GPS or Global Positioning System, which is entirely based on satellites.
Thus, any device can determine the exact location of anywhere on the earth.
In smartphones, the hardware component GPS receivers-antennal combined with excellent software algorithms used to interpret signals transmitted from Earth satellites as part of the complete solution.
Thus, turn-by-turn navigation, location sharing, workout tracking, and lots more only come from the fingertips.
Transformation in an industry such as the transport industry, logistics, or even social networking is witnessed from the introduction of GPS technology.
Indeed, GPS has become an essential technological component of modern living.
The potential future changes promise much more since GPS technologies will undergo speed and accuracy.
Improvements along with integrating developments such as augmented reality and 5G connection.
How GPS Locates Your Position
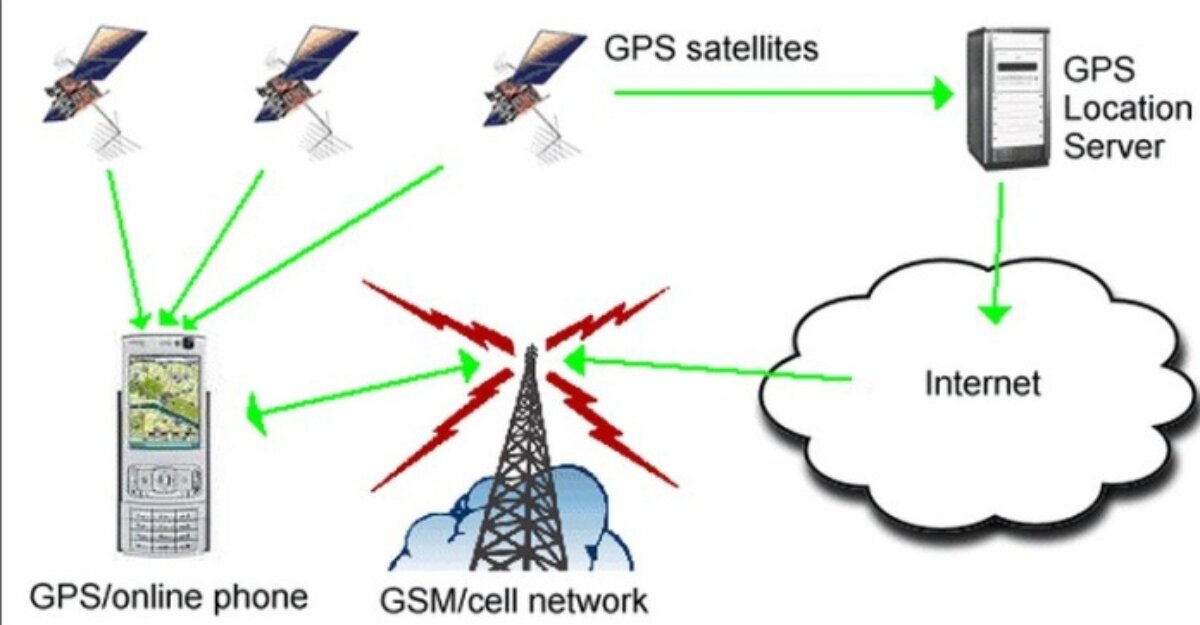
All satellites generate signals indicating their location and exact timing from which the signals are generated while orbiting the Earth.
In the triangulation process, the GPS receiver in your mobile device picks up signals from three to four satellites.
You may be Read Also: “8 Reasons the Moto Edge 60 Pro Redefines Flagship Smartphones”
According to the delay of reception of the signal by its device, the distance of the satellite from the device can be measured.
Using these measurements, the mobile finds an exact location of geographical position through a calculation. This process is called trilateration.
Accuracy is determined by factors like strength of signals, how many satellites are being visible, and their conditions. Generally, clear skies and fewer obstructions are favorable for accuracy.
Combined GPS and cell tower/Wi-Fi network location data for the A-GPS aids in achieving improved accuracy and better speed. A-GPS is especially useful for densely built-up areas where signals can be blocked.
Key Components of GPS in Smartphones
Smartphone GPS is a seamless combination of hardware and software that provides accurate and reliable location services.
So here are some of those major components:
Hardware Integration
- GPS Receiver: A special chip embedded inside the phone that receives signals from satellites and calculates a position.
- Antenna: Designed for optimum use even in the hardest environments to pick up GPS signals.
- Processors: The advanced processors that do these calculations are fast enough to keep the processing up to date so that real-time locations can be easily given and updated.
Read Here: What Is GPS In Hindi | How GPS Works In Hindi
- Battery: Since GPS features are pretty battery consuming inside the smartphones, they maximize the usage of batteries supporting this functionality.
Software Integration
- Operating System: Integrated GPS platforms such as Android and iOS come with additional built-in GPS frameworks which the apps can then access for location-based data.
- Mapping Applications: Google Maps or Apple Maps is the software that converts the GPS data to provide navigation, traffic status reports, and the nearby points of interest.
- Assisted GPS (A-GPS): Added speed and improvement in location acquisition and accuracy to location fixing from data using satellites and cell towers and possibly Wi-Fi radios.
- Advanced Algorithms of Artificial Intelligence: The next generation of algorithms acquires, interprets, and reduces interference to improve location accuracy for GPS signals in the future.
Benefits of Smartphone GPS

Smartphone GPS technology has completely shunned the way of normal life founds its own space in bringing together navigation, connectivity, and coordination of daily activities.
Indeed, here are some real-world value propositions that drive home the importance of these applications:
- Navigation and Directions– GPS is the major tech backbone of mapping applications
like Google Maps and Apple Maps providing turn-by-turn directions while updating traffic and alternative routes ensuring a hassle-free travel experience.
- Fitness and Health Tracking– Most applications getting momentum in health and fitness activities have really relied on GPS to assess and record outdoor activities
like running, cycling, and hiking while getting into a format of feedback reflecting distance, speed, and routes to encourage you in achieving your set goals.
- Location Sharing: using GPS, users can share with their friends, family, and units for safety and convenience while traveling or meeting in groups.
- Ride-Hailing Services: Services such as Uber and Ola have made use of GPS to get the best possible tracking of picking up point to drop-off point to make travel more efficient and user-friendly.
- Geotagging in Photos: This makes possible by using the smartphone GPS geotag your photos with the location by creating detailed memoirs of places you have visited.
- Emergency Services: GPS safety measures as the location of an individual in distress during emergencies can be quickly found and accessed by the first responders.
- Logistics and Delivery Tracking: This has revolutionized e-commerce and food delivery by tracking deliveries or parcels being delivered with current feasibility on location.
Challenges and Limitations of GPS

Transformative technology, but it does bear limits and challenges that can affect GPS functioning. The following are some factors:
Signal Interference
Tall buildings, thick foliage, and tunnels can scatter, weaken or block GPS signals; thus, producing a lesser degree of accuracy in urban or covered environments.
Weather such as heavy rain or thick clouds sometimes weakens the signal, thus degrading the performance.
Power Drain
GPS activities are quite power-consuming such that the smartphone battery runs out faster when GPS is used extensively for navigation or tracking.
Smartphone should have a power management system that is very efficient in ensuring that GPS does not interfere with battery performance.
Urban Environment Accuracy
In major cities, signals can get reflected by buildings or other structures, causing mistakes known as “multipath errors.”
Dependence on Satellites
GPS cannot work properly without clear “sight” of satellites; thus it is not very reliable when used indoors or under satellite constellation shadows.
Initial Position Fix Time
In some environments, obtaining a location fix-time to first Fix (TTFF) has a long time requirement, which is more so in standard GPS systems.
Limited Indoor Navigation
Normal GPS is incapable of providing accurate position data indoors and needs the assistance of other technologies like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth beacons for navigation.
Security Foes
There exist potential threats of spoofing and jamming of GPS signals for certain applications which can be detrimental particularly for sensitive industries.
Conclusion: GPS in the Future of Smartphones
Ever since the start of its evolution, GPS has triggered fresh developments in smartphones, improving how we access the world.
Today’s smartphones, with the addition of an Assisted-GPS (A-GPS) feature, dual-frequency GPS technology, and 5G, can afford.
Unparalleled precision and speedy, reliable location services comparison with any surrounding technological advances.
Emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and machine learning are also going to establish a revolution in GPS applications.
AR, for instance, projects navigation elements onto an actual world surrounding it, giving an end user an easy yet interesting way of consuming navigation.
While redundancy and improved location accuracy can be found in artificial intelligence, which largely increases efficiency in power consumption of the involved devices.
Such new things include indoor GPS solutions and the whole concept of Bluetooth beacons.
An example of these extends the realm of GPS into the indoor spatiality of malls, airports, and other complex
Environments that such a technology can offer if it does not have measures of opening new doors to seamless navigation in places traditionally denied accessibility to it through GPS signals.
Thus, GPS can be said to play an important role in industries like transport, healthcare, smart cities, etc.
As it is going to be the backbone for smart logistics and autonomous vehicles along with real-time Emergency response systems.
Indeed, the future of GPS in smartphones is promising as with this thriving mobility.
There will be greater connectivity, convenience, and integration with newer technologies increasingly molding the digital landscape.